The constellation Cetus
Características
- Nome latino
- Cetus
- Hemisfério
- Ambos os Hemisférios
- Visibilidade
- September - January
- Área
- 1231 deg²
- Estrela mais brilhante
- Diphda (HIP number 3419)
- Especialidades
- Galaxies, planetary nebula
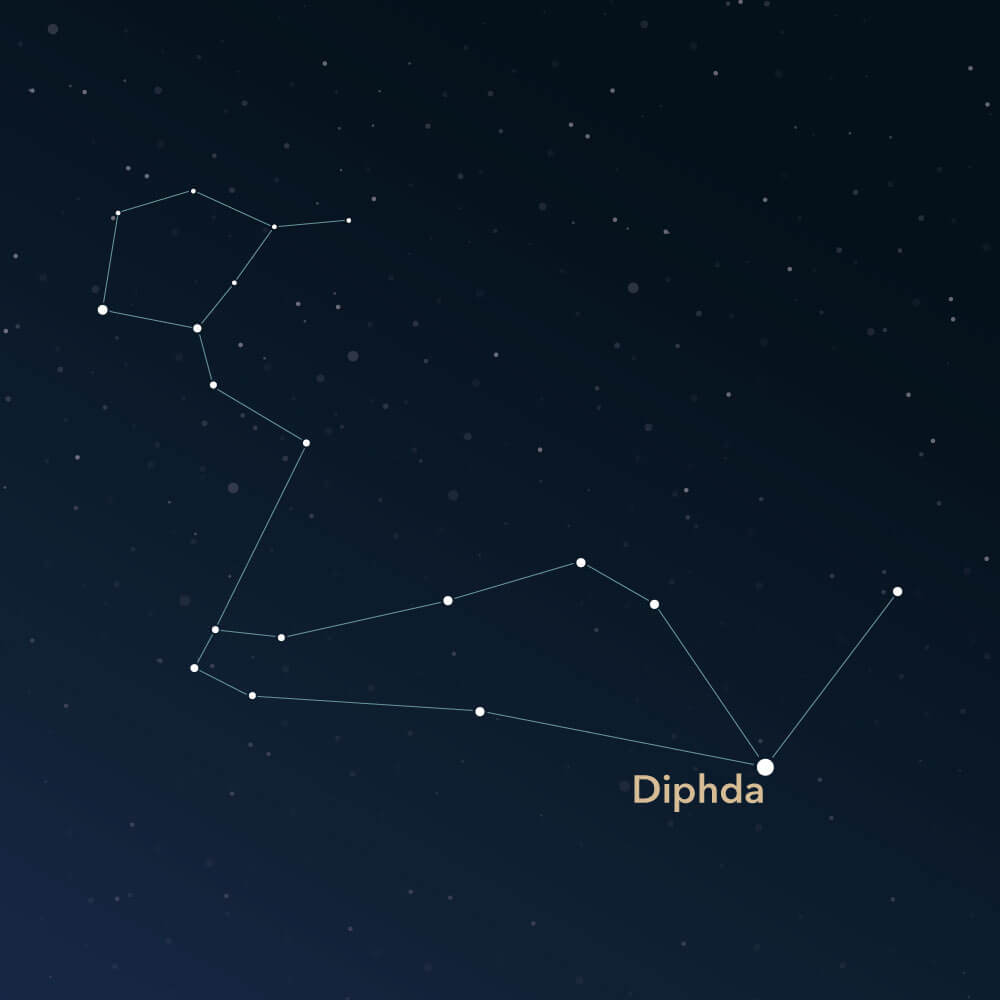
The Cetus symbolizes a sea monster or even a whale and is a large but inconspicuous constellation that stretches across both hemispheres. It includes several deep-sky objects to observe. The Greco-Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy included it in his list of 48 ancient constellations.
Hemisphere, visibility, and area
The constellation Cetus lies on the celestial equator and is visible from earth between 65° N and 80° S latitudes. In the northern hemisphere, it can be seen almost fully in the night sky, up to the northern polar circle. In the south, it is visible far into the Antarctic region.
The months from September to January offer the best view of the constellation. It is spread over an area of about 1,231 square degrees, making it the fourth-largest constellation among all other 88 constellations.
However, the Cetus is not particularly conspicuous. In its area, mostly faint stars can be found, with only two having an apparent magnitude brighter than 3. The brightest star is β Ceti (Beta Ceti), also known as Diphda or Deneb Kaitos. It is an orange giant star located approximately 100 light-years from earth, with an apparent magnitude of roughly 2.04 mag.
To find the Cetus in the night sky, neighboring constellations provide a good orientation. It is adjacent to four constellations that lie on the ecliptic and are particularly known in astrology: Aries, Pisces, Aquarius, and Taurus. The Sculptor, the Fornax, and the large constellation Eridanus are also located in close proximity.
Specialties in the constellation
In the celestial area of Cetus, there are a handful of galaxies and a planetary nebula.
The brightest galaxy is identified by the catalog number NGC 1068 or M77 (Messier 77). It is a radio galaxy with an active galactic nucleus at its center. The distance to the Milky Way is estimated to be around 50 million light-years, and its apparent magnitude is roughly 8.9. Thus, professional equipment, such as a telescope or prism binoculars, is necessary to observe the galaxy. M77 is the farthest object that the French astronomer Charles Messier cataloged.
Mythology
In Greek mythology, the constellation Cetus represents the sea monster in the story of the beautiful Andromeda. Her mother, Cassiopeia, angered Poseidon when she claimed that she and her daughter were more beautiful than the Nereids. As a punishment, Poseidon sent a sea monster to ravage the shores of the kingdom of Cepheus.
To protect his subjects, king Cepheus consulted an oracle that advised him to sacrifice his daughter Andromeda to appease the wrath of the sea god and his wife. Thus, he chained his daughter to a rock, where she waited in fear of her fate. As Cetus approached the maiden to devour her, the hero Perseus appeared and saved her from death.
To commemorate this tale, all the characters involved were set as constellations in the sky.
PublicadoLeia mais artigos interessantes

An overview of all 88 constellations
Learn more about all 88 constellations and read interesting information about the mythology, visibility, and features.

Aplicativo Planetário
Descubra o céu noturno com nosso aplicativo de planetário!
Disponível para iOS e Android.
Nomeie uma estrela na constelação Sea Monster, Whale
Name a star in a constellation and create something that lasts for eternity.